Last week we attended the annual “Tri-Party” Transportation Conference in Red Deer, Alberta. It was good to catch up with many of the suppliers, clients, and other engineers we work with on so many projects. It was also great to hear presentations about issues affecting the industry, like the state of environmental permitting and the […]
AAMDC Convention 2014
Thanks to all of our clients (and potential clients) who stopped by our booth at the AAMDC convention in Edmonton this week. It was great to see all of you. Here are a few pictures. I always love to get that glimpse of what’s on the minds of our clients and this is a great […]
Drainage Design in Southwestern Alberta
Alberta’s southwestern corner is a small area which produces by far the highest amount of precipitation in the province. To see how extreme the precipitation differences are, just take a look at Alberta Transportation’s “Runoff Depth Map” (to the right; Click to enlarge) which governs one of the methods used to determine design flows for […]
Geothermal Heating: Pros, Cons, and Economics
Geothermal energy is produced from heat inside the earth. The temperature at the earth’s core is approximately 5,400 degrees Celsius (9,700 degrees Fahrenheit). From the surface, a few degrees of heat can generally be observed at depths of 20 – 30 m (65 – 100 ft), although this is highly variable. Pros Environmentally friendly Renewable […]
How to Calculate a Water Hammer
Last summer I built an underground sprinkler system for my lawn. As I flipped the switch for the first time and beamed with pride at my wonderful creation, I couldn’t help but notice the loud thud whenever one of the valves closed. Lo and behold (insert joke about engineer building projects here), this is a […]
Fluid Dynamics
Fluid dynamics refers to the study of fluid in motion. It includes fluid moving through pipes, measurements with venturis and orifices, and other motion-related topics such as lift and drag, and pumps. Reference The field of fluid dynamics is a subcategory of fluid mechanics. It’s sibling is fluid statics. In practice, the field of fluid […]
Acceleration Due to Gravity
The normal values for gravitational acceleration used in physics and engineering are: g = 9.8066 m/s2 g = 32.1740 ft/s2 Poles and Equator Because g varies from the poles to the equator, here are the extreme values: North and South Poles: g = 9.832 m/s2 = 32.26 ft/s2. Equator: g = 9.780 m/s2 = 32.09 […]
How to Calculate Relative Density
Relative Density is the ratio of the density of a substance to a specified reference density. $latex D_r = \frac{\rho_s}{\rho_{ref}}&s=2$ Where: Dr = Relative Density (dimensionless) ρs = bulk density of soil (kg/m3 or lb/ft3) ρref = bulk density of reference (kg/m3 or lb/ft3) Often, the reference density is that of water, 62.4 lbs/ft3 or […]
How to Calculate Specific Gravity
Specific Gravity is the ratio of the density of a soil to the density of water. $latex SG = \frac{\rho_s}{\rho_w}&s=2$ Where: SG = Specific Gravity (dimensionless) ρs = bulk density of soil (kg/m3 or lb/ft3) ρw = bulk density of water (kg/m3 or lb/ft3) = 1000 kg/m3 (62.4 lb/ft3) Specific Gravity of Various Substances Substance […]
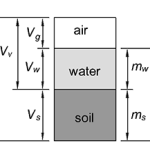
How to Calculate Bulk Density
Bulk density, also called soil density, is the ratio of the total mass of a soil to the total volume. $latex \rho = \frac{m_t}{V_t}\newline\newline =\frac{m_w + m_s}{V_g + V_w + V_s}&s=2$ Where: ρ = bulk density (kg/m3 or lb/ft3) mt = Total mass (kg or lbs) mw = Mass of water (kg or lbs) ms […]